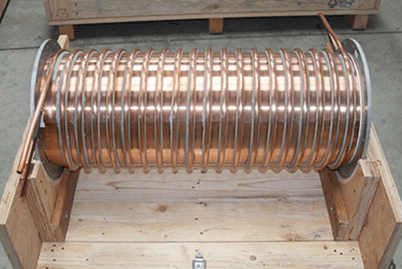
Electric coils conduct energy and allow for inductance to counter or control the flow of current. The coils are constructed from wires (made from conductive materials like copper) which may be wound around a cylinder, disk, or toroid-shaped ferromagnetic core or as a self-supported structure (wire only). While electric coils operate based on simple principles, manufacturers can design and construct electric coils with different capabilities for a wide range of consumer, commercial, and industrial applications. At Custom Coils, we specialize in producing coils for the following industries:
- Image and Scanning Industry
- Medical Industry
- Power Generation Industry
- Satellite and Aerospace Industries
- Semiconductor Processing and Test Equipment
Electrical Coil Design
Manufacturers consider these four design elements to create custom electrical coils and overcome thermal challenges:
Wires
The basis of any electromagnet starts with a conductor wrapped in a defined shape/structure. The shape, thickness, and length of the wire all factor into the coil’s magnetic field, the energy loss, and the ability of the coil to complete different functions. The resistance of the wire and the insulation required for the coil may dictate the type of wire used.
For electrical coils used in harsh or demanding environments, electroplated wires can withstand potential deterioration. Electroplating processes coat the wires with materials like gold, nickel, or silver, as well as an insulative coating.
Insulation
Electrical coils also need insulation to isolate the windings as well as protect the wires from extreme heat and thermal damage. It sits between the wires so they don’t make contact and fail due to shortage. Manufacturers can help select the right type of insulation for an electrical coil based on the coil’s anticipated thermal capacity, the wire gauge, and the product’s applications.
Types of Coil Winding
Manufacturers wind wires around the ferromagnetic core in a precise shape and design to fulfill different functions. The type of coil winding in an electrical coil will be determined based on the:
- Insulation
- Quality
- Inductance
- Type of magnetic field being generated
Core Material
The coil’s core is an essential element. Different types of core materials produce magnetic fields of different strengths and affect the coil’s inductance.
Thermal Challenges
Cooling and Thermal Control
Often the dimensional constraints and operational requirements of the electromagnet produce a coil that will heat up beyond temperature limits of the materials or system it is operating in.
A coil’s magnetic field is directly driven by the number of turns on the coil and the amount of power input (amps). Typically, the magnetic field requirements for the coil drive specific turn count and power requirements to generate the desired field; however, the coil dimensions constrain the number of turns that can be wound in the given dimensional space. This will require higher power input to the coil and may drive the temperature beyond the material or operational limits. Additional cooling may be required to draw heat out of the coil.
Cooling Applications:
Heat Sink: A structural holder (as defined above) can often act as a heat sink to draw heat away from the coil. For example, a coil wound in a copper bobbin (copper has a high thermal conductivity) will conduct heat out of the coil through the bobbin. Often times, heat sinking material is used, along with convection (fans, air flow) to provide enough cooling flow out of the coil.
Heat Sink with Cooling: Similar to above, if heat sink with convection not enough to control temperature, a cooling path can be designed into a structural holder for the coil.
In-line Cooling: Hollow core conductors are used to wind the coil and act as the electrical path and the cooling path. This allows for cooling to run through the coil itself and they are typically used in high-power applications.
Copper Tube Cooling: Depending on the size of the coil, copper tubing can be applied on the ID, OD, or in the center of the coil windings.
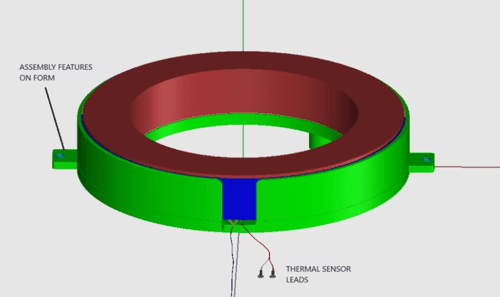
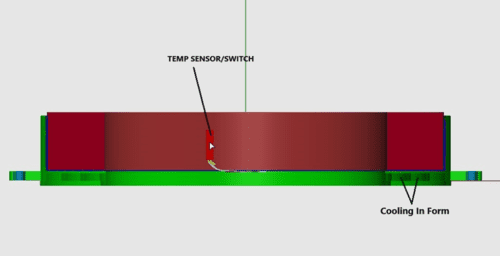
Temperature Sensor/Cut-off
Thermal sensors can be applied to a coil to monitor temperature and control operation when a coil gets too hot or rises beyond operational limits.
Sensor Types
- Thermocouples: Thermocouples can be applied externally on the coil or applied during winding at various internal points in the coil. Thermocouples monitor temperature and allow user flexibility in regard to actions taken when various temperature situations occur. They are typically integrated into the power supply system to monitor the coil temperature and determine whether to decrease power and/or shut down the system at various temperatures.
- On/Off Temperature Switch: These are on/off switches made to shut off power at a specified temperature. These can typically be applied externally on the coil and/or in line with the lead wire to the power source.
Custom Electrical Coils From Custom Coils
At Custom Coils, we specialize in creating high-performance electrical coils with sufficient cooling solutions for long-term operations. Contact us today to learn more about our capabilities or request a quote to start your order.